Smart-Particle & Bead-Free DNA Detection
Tech ID: 11-011 & 11-027
Inventors: Dr. Steven Ruggiero, Dr. Carol Tanner
Date added: October 20, 2020
Overview
A rapid species-specific DNA detection and quantification method based on laser transmission spectroscopy.
Technology Summary
DNA detection is essential to many industries, from identifying invasive-species in environmental field research to identifying human pathogens in medical diagnostic testing, from assisting in new drug development to ensuring the safety of our food supply. Established techniques for genetic profiling (PCR, micro-arrays, fluorometric detection) generally face limitations of high cost, low throughput, reliance on electrical/chemical indicators, time-consuming sample preparation, and inability to distinguish between target and non-target organisms.
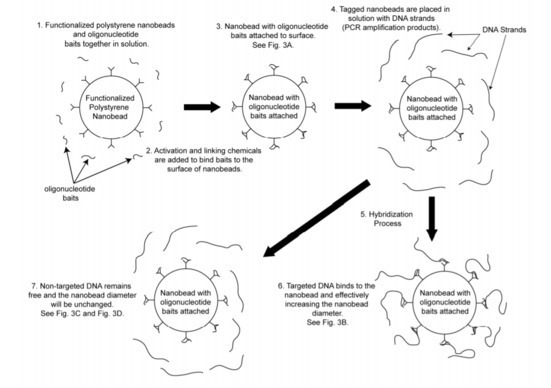
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed two rapid methods of detecting and measuring the presence and quantity of species-specific DNA in solution. Both methodologies are based on the principle of functionalized ‘smart’ particles that attract target DNA and each uses Laser Transmission Spectroscopy to measure the size, shape, and number density of nanoparticles. The Smart-Particle DNA Detection technology operates by functionalizing nanoparticles to hybridize with target material, introducing the functionalized nan0particles in the solution of interest, and hybridizing the functionalized nanoparticles with any present species-specific target material. The Bead-Free DNA Detection method results in a detectable change (ie. color change) upon hybridization of sets of oligonucleotides attached to nanoparticles with target nucleic acid sequences. Both the Smart Particle and Bead-Free DNA Detection techniques developed at Notre Dame are better alternatives to MAD, PCR, and other genetic profiling methods for their ability to rapidly detect and quantify species-specific DNA from small sample sizes.
Market Advantages
• Detect and quantify DNA particles from a small sample.
• Save time – less time-consuming steps required to analyze DNA than with MAD and PCR.
• Distinguish between target and non-target DNA.
Publication
Ultrasensitive, Quantitative, and Rapid DNA Detection By Laser Transmission Spectroscopy.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029224
Intellectual Property
US Patent 9,657,336
US Patent 9,447,456
Technology Readiness Status
TRL 3 – Experimental Proof of Concept
Contact
Richard Cox
rcox4@nd.edu
574.631.5158