Functional Nanosurfactant Systems for 3D Printing of Nanomaterial Inks
Tech ID: 20-054
Inventors: Dr. Yanliang Zhang, Dr. Minxiang Zeng
Date added: June 30, 2020
Overview
A colloidal nanosurfactant system to exfoliate, stabilize, and formulate 2D nanomaterials in water-based inks for 3D printing applications.
Technology Summary
3D and 2D printing techniques have found a number of applications in electronics, sensors, biotechnology, and material synthesis/patterning. Currently, multi-dimensional printing techniques using nanoscale materials are gaining increasing attention for fast prototyping and large-scale manufacturing of functional devices. Functional nanomaterials have potential to be directly converted into final device patterns on both 2D and 3D substrates with superior spatial resolution. Therefore, printable nanomaterials possess promising potential for a wide range of applications including electronics, sensors, battaries, and flexible/wearable devices. However, current ink formulations of nanomaterials involve toxic and expensive organic solvents that often require extra removal steps and additional polymers to strengthen the mechanical bonding of the printed product. Therefore, a new generation of water-based nanoparticle inks must be developed to improve the efficiency, quality, and safety of 2D and 3D printing.
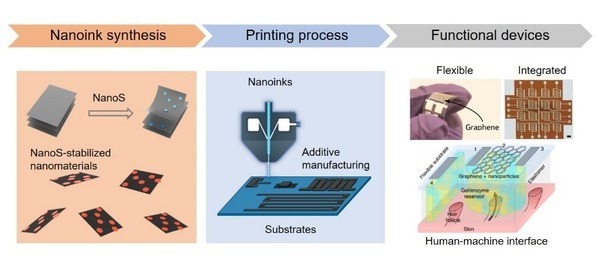
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have recently developed a novel water-based ink formulation with surface-active nanosurfactants for 2D and 3D printing applications. This printing technique involves the synthesis of the graphene quantum dot nanosurfactant, nanomaterial ink formulation, and aerosol jet printing. The Functional Nanosurfactant Systems for 2D and 3D Printing of Graphene and 2D Nanomaterials developed by the University of Notre Dame is a superior alternative over conventional surfactant systems because of higher spatial resolution of the printed product, enhanced photoconductance of ink materials, bandgap engineering, improved film robustness, and the surfactant does not need to be removed for final device fabrication.
Market Advantages
• Reduces interfacial tension and stabilizes colloidal nanoparticle systems.
• High colloidal stability of inks.
• Rapid fabrication of complex device structures with high spatial resolution.
• Improved mechanical robustness of printed films.
Market Opportunity
• Broad applications in sensors, energy conversion/storage devices, and flexible and wearable electronics.
• Functional inks of various nanomaterials for 2D and 3D printing.
• Super-robust thin films and coatings.
Technology Readiness Status
TRL 3 - Experimental Proof of Concept
Contact
Richard Cox
rcox4@nd.edu
574.631.5158