Point-of-Care Digital Droplet PCR
Tech ID: 21-038
Inventors: Liao Chen, Hsueh-Chia Chang, Chenguang Zhang, Vivek Yadav
Date Added: June 9, 2021
Overview
Rapid point-of-care digital droplet PCR quantification method at low viral loads for saliva and swab testing.
Technology Summary
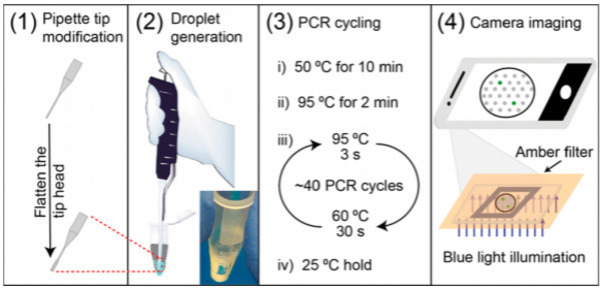
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) remains the gold standard for virus detection from nasopharyngeal swabs and/or saliva samples. However, the need to conduct this assay in laboratories and the resulting long transport time have become a bottleneck on the control of a rapidly spreading pandemic with high positivity rates. Even with its expensive and lab-bound optical instruments, the false negative rate of rt-PCR detection especially for the newly infected samples with low viral concentration is not satisfactory. It is known that, compared with rt-PCR, droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) has better sensitivity by partitioning the samples into large numbers of droplets to enrich the virus RNA and also mitigate the influences of PCR inhibitors. Their simpler optical detectors also suggest ddPCR products can be used at the point-of-care (POC), without transportation to laboratories. Nevertheless, a viable rapid POC ddPCR COVID screening test has yet to be reported. Alternatives to the bulky and expensive micropumps in commercial products have been proposed. However, the main challenge for POC ddPCR is the droplet size and the related lab-bound optical detection platform.
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have recently developed a novel digital droplet PCR method that can be used for POC quantification at low viral loads. It utilizes a specially designed pipette instead of bulky micropumps or complex microfluidic devices for droplet generation. The large droplets generated by the pipette allow visual or smartphone detection of the signal, without expensive and bulky optical instrumentation. Both of these modifications speed up the PCR assay to less than an hour under optimized conditions and removes the need for results processing in a centralized lab. This new design is nearly as fast as antigen and antibody tests. The sensitive and rapid POC digital droplet PCR method developed by the University of Notre Dame has applications for epidemic control and low-resource developing-world applications for swab and saliva samples.
Market Advantages
- Rapid point-of-care at a low RNA copy number range
- Portable kit without heavy equipment
- Fast results (<1 hr) & no need for a centralized lab
Market Applications
- PCR Global Market - $4.5B, 17.5% CAGR
- Saliva tests for viruses and other pathogens
Technology Readiness Level
TRL 4 - Lab Validation
Publication
Elliptical Pipette Generated Large Microdroplets for POC Visual ddPCR Quantification of Low Viral Load. Anal Chem. 2021 Apr 27;93(16):6456-6462. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00192
Intellectual Property Status
Patent Pending