A New Class of Quinazolinone Antibiotics
Tech ID: 13-023
Inventor: Dr. Mayland Chang
Overview
A short description of ND13-023, describing a class of quinazolinone antibiotics that can be used to treat and prevent MRSA bacterial infections.
Technology Summary
Staphylococcus aureus ( S aureus) is a leading source of serious bacterial infections in humans. A growing nmber of S. aureus strains are showing increasing resistance to current antibiotics and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is responsible for 126,000 hospitalizations and 19,000 deaths in the US each year. Therefore, the development of new antibiotics for treatment of MRSA infections is essential, especially the development of orally-available antibiotics.
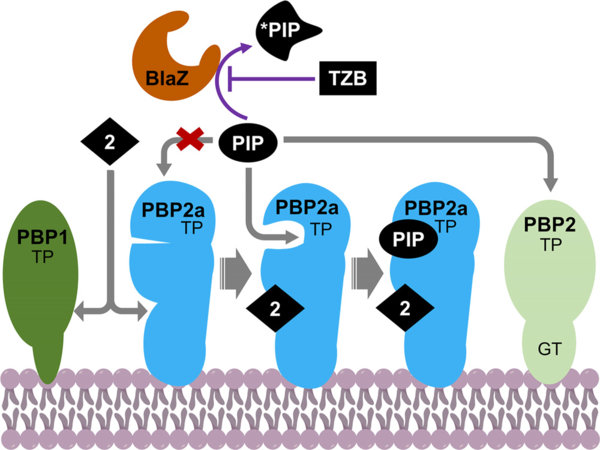
University of Notre Dame researchers have discovered a new orally active class of quinazolinone antibiotics that shows effective excellent activity against S. aureus strains, both methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains, both in vitro and in vivo. The antibiotics bind to PBP2a and PBP1 as targets. The quinazolinone class synergizes with β-lactam antibiotics. The combination with piperacillin and tazobactam kills MRSA. For the synergistic activity, the quinazolinones have a unique mechanism of action, binding to the allosteric site of PBP2a and opening the active site of PBP2a where the β-lactam antibiotic piperacillin can now bind for covalent inhibition.
Market Advantages
Circumvent known MRSA resistance mechanisms
Display in vitro efficacy
Display in vivo efficacy in mouse- models of infection
Synergistic with β-lactam antibiotics
Intellectual Property
US Patent 9,776,975
(Quinazolinone Antibiotics)
Technology Readiness Status
TRL 4 - Lab Validation
Publications
Discovery of Antibiotic (E)-3-(3-Carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl) quinazolin-4(3H)-one. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b00056
The Quinazolinone Allosteric Inhibitor of PBP2a Synergizes with Piperacillin and Tazobactam against Methicillin-resistant
S. aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02637-18.
Structure-Activity Relationship for the 4(3H)-Quinazolinone Antibacterials. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5011-5021.
Contact
Richard Cox
574.631.5158